GPS Asset Tracking Systems: Capabilities, Costs & Best Solutions
GPS asset tracking involves attaching battery-powered GPS trackers to physical assets like vehicles, heavy equipment, machinery, and containers. This enables live tracking using a global positioning system to monitor and track assets in real time.
A GPS asset tracking system provides real-time location data, geofencing capabilities, and integration with digital platforms like Asset Tracking Software. It is designed to address three main pain points for equipment managers:
- Location accuracy: Know where assets are located indoors and outdoors with integrated Wi-Fi and GNSS trackers.
- Safety and security: Prevent theft of high-value assets and ensure fast recovery.
- Visibility: See real-time location data for all vehicles and equipment in one mobile app.
Affordable hardware and rapid contact signalling make GPS asset tracking systems perfect for industries with multiple high-value moving equipment. That includes construction, healthcare, transport, and logistics.
Easily shortlist GPS Asset Tracking Systems for the live, real-time tracking of vehicles and mobile equipment, preventing theft and improving visibility.
What Type of Assets Do You Want to Track?
How Does GPS Asset Tracking Work?
There are three key components to a GPS asset tracking system:
- The GNSS: A constellation of around 24-32 GPS satellites orbiting the Earth at an altitude of approximately 20,200 kilometres.
- GPS tracking devices: Receivers capture live tracking data and process signals from multiple satellites.
- GPS asset tracking system: A tool that captures transmitted data and displays it on a live map.
GPS trackers consist of an antenna and a receiver. These tags communicate with the GNSS to send and receive data back and forth.
In terms of asset tracking, tags are affixed to equipment and transmit location data to an asset tracking system.
When communicating with the GNSS network, GPS trackers use a process known as trilateration. This phase is where a series of at least three satellites determines an asset’s latitude, longitude, elevation, and time.
What Are the Best GPS Asset Tracking Systems?
Itemit
![]()
A cloud-based GPS asset tracking solution for individuals, teams, and departments. This is a simple, easy-to-use system that enables quick self-setup starting at £21 per month. Itemit provides its own GPS trackers for high-value assets that are configured in different workspaces quickly.
Industries: Construction, Healthcare, Trades, Domestic services, and Entertainment
Deployment: Cloud-based, Mobile App, Desktop
Visilion by Sony
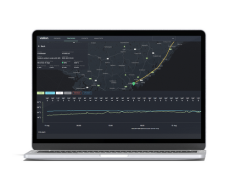
A real-time GPS asset tracking solution designed with supply chain visibility in mind. This is ideal for organisations tracking assets or cargo in real-time, requiring precise location and condition monitoring data. Starting at £20 per tracker, per month, Visilion is used on high-value assets that are time-critical and sensitive.
Industries: Logistics and distribution, Packaging, Construction, Automotive, and Consumer products
Deployment: Desktop, Tablet, Mobile
Timly

GPS asset tracking is a key feature of the Timly professional pricing plan, which starts at £445 per month. The plan provides real-time tracking across multiple sites and personnel. This solution is ideal for businesses with high-value assets and rapid asset allocation and movement.
Industries: Government, Education, Engineering, Construction, Manufacturing, and Recreation
Deployment: Cloud-based, Mobile app, Desktop
Lime
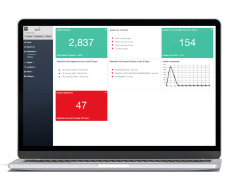
A GPS asset tracking system for complex scenarios and workflows. The system is ideal for companies with a high volume of mobile assets and a first-year budget of at least £25,000. Features an auto-scanned tracking zone feature for accurate location tracking.
Deployment: Cloud-based, Mobile app, On-premise, Desktop
Assettrac
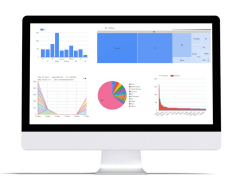
A tracking solution with GPS functionality to deliver location- and status-driven reporting. Assettrac provides full implementation that includes hardware (GPS trackers) and software. Prices start from £2,500 per annum.
Industries: Healthcare, IT, Education, Government, and Domestic services
Deployment: Cloud-based, web-based (desktop)
Shortlist the UK’s best GPS Asset Tracking Software products
What Type of Assets Do You Want to Track?
How Much Does a GPS Asset Tracking System Cost?
The cost of a GPS asset tracking system varies depending on:
- Type of hardware needed
- Scale of deployment
- Level of software functionality required
- Implementation requirements (time-based and quantity)
Hardware costs range from £50 to £200 per GPS tracker. This depends on factors like durability, battery life, and features like real-time tracking, geofencing, and motion alerts.
Rugged, weather-resistant models and solar-powered options tend to sit at the higher end of the spectrum. Basic battery-powered units are more affordable.
GPS Asset Tracking Software pricing is generally subscription-based. Providers charge a monthly fee per tracker or user, ranging from £5 to £15. Some providers, like Visilion by Sony, charge a flat monthly rate per device.
This includes both tracking hardware and access to the software platform. These systems are designed for easy onboarding and come with intuitive mobile apps.
For small businesses, cost-effective self-service systems such as itemit or EZOfficeInventory start at around £21 per month. These offer access to core tracking features, mobile apps, and support without complex setup or integrations.
Medium-sized businesses may pay slightly more for added capabilities such as usage reporting, maintenance scheduling, and geofencing.
While enterprises often benefit from volume discounts and custom integrations, including API access and multi-user environments.
Although the cost of a GPS asset tracking system can seem a lot at first, it’s important to understand return on investment potential. 31% of GPS tracking users reported a positive ROI within the first 6 months
What Are 4 Stand-Out Features of GPS Asset Tracking?
1. Mobile App for Real-Time Data Access
Modern GPS asset tracking systems feature mobile and cloud-based apps. These allow managers to monitor assets in the office, on-site, or while travelling.
Users can log in via smartphone or tablet to access live data on asset location, running time, idle hours, and utilisation.
This instant visibility helps identify under-utilised equipment for possible decommissioning and enables precise scheduling of planned maintenance. The results are reduced downtime, optimised asset usage, and more informed, data-driven decisions.
2. Geofencing Capabilities
Geofencing enables users to define virtual boundaries for specific job sites or zones.
If an asset enters or leaves these zones unexpectedly, the system triggers an alert. This feature is useful for theft prevention, site compliance, and keeping track of multi-site operations.
It ensures assets are where they should be, flagging when they’re not.
3. Real-Time Movement and Usage Alerts
GPS tracking systems send instant notifications based on asset activity. Examples include unexpected movement, engine start-up outside of hours, or excessive idle time.
These real-time alerts help businesses respond quickly to unauthorised uses or emerging issues, improving security and accountability across the board.
4. Rugged and Weather-Resistant Tracking Hardware
GPS trackers are engineered for durability, with weatherproof and shock-resistant casings that withstand extreme conditions.
Whether exposed to heavy rain, dust, vibration, or temperature swings, tracking devices are built to continue transmitting reliable data.
This ensures consistent performance on construction sites, in remote field locations, and during rough transport.
This makes trackers suitable for industries where equipment faces constant environmental stress and demanding usage.
How Easy Is It to Implement GPS Asset Tracking Software?
In short, implementing GPS asset tracking procedures is an effortless process. This ease is due to low installation barriers, scalable pricing, and easy-to-use third-party systems.
Most systems are designed for quick deployment with minimal disruption. At the core are the GPS trackers themselves. These compact devices are mounted on assets using industrial adhesives, magnetic bases, or bolt-on fixtures.
Many GPS trackers are battery-powered and require no hardwiring, which simplifies installation further.
Battery life varies by model and reporting frequency. Basic trackers can last 2–3 years, while advanced models with motion sensors or solar charging can extend battery life up to 5–7 years. Some systems are hardwired into vehicles or equipment for continuous power.
In terms of price, GPS trackers range from £50 to £200 per unit, depending on features like real-time tracking, tamper alerts, or ruggedisation.
Most GPS asset tracking providers offer user-friendly mobile and desktop apps. These apps come with guided setup and support during rollout, ensuring a fast and straightforward onboarding process.
Types of GPS Trackers and When Best to Use Them
GPS trackers come in several types, each suited to different asset tracking needs. They include:
- Battery-Powered Trackers
- Hardwired Trackers
- OBD Trackers
- Solar-Powered Trackers
- Portable Trackers
- Bluetooth Asset Tags
Each has their own unique capabilities that are used for different processes, as displayed in the comparison table below:
Tracker Type | Power Source | Typical Use Case | Installation | Battery Life / Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Battery-Powered | Internal battery | Trailers, containers, mobile equipment | Adhesive, magnetic, or bolted on | 6 months to 7 years (depending on use) |
| Hardwired | Vehicle or machine power | Vehicles, heavy equipment | Wired into ignition or battery | Continuous (vehicle-powered) |
| OBD Trackers | OBD-II port power | Light commercial vehicles | Plug-and-play into OBD port | Continuous while vehicle is on |
| Solar-Powered | Solar panel + internal battery | Remote or infrequently used assets | Mounted on asset surface | Long-term with sufficient sunlight |
| Portable Trackers | Rechargeable battery | Temporary tracking, valuables in transit | Carried or attached with clip | A few days to weeks |
| Bluetooth Asset Tags | Coin cell battery | Indoor or short-range tracking | Attached via adhesive or strap | 6–24 months |
3 Real-World Examples That Show the Value of GPS Asset Tracking
1. World Trade Center Cleanup Project
GPS tracking technology played a vital role in the debris removal project at the World Trade Center site.
GPS systems were used to track thousands of truckloads of debris leaving Ground Zero, ensuring accurate documentation, security, and efficiency. This included 200 vehicles, responsible for removing 1.8 million tonnes of material.
By equipping trucks with GPS and integrating tracking data, the team prevented unauthorised dumping, validated haul routes, and enhanced coordination.
2. Improved Customer Service For British Gas
British Gas achieved a strong return on investment (ROI) by implementing a GPS fleet tracking system. It cut its fleet size by 10% and saved £14 million over five years. These savings were driven by improved vehicle utilisation and route optimisation.
The system also enabled more accurate ETAs for customers, increasing customer satisfaction.
3. Eastern Distribution’s Quick Theft Recovery
Eastern Distribution significantly reduced vehicle theft by implementing GPS tracking across its fleet. The system enabled real-time location monitoring, allowing stolen vehicles to be recovered within hours.
Over time, the presence of GPS acted as a theft deterrent, lowering the frequency of incidents. As a result, the company benefitted from reduced insurance premiums.
How Does GPS Asset Tracking Compare to RFID and Barcode Systems?
Asset tracking solutions range from RFID asset tracking to barcodes and QR codes. Ultimately, the decision to implement a solution comes down to what you require.
It’s also important to understand the key differences between tracking solutions. In terms of cost, durability, range, use, and battery life.
Technology | Hardware Cost | Durability | Range | Battery Life |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Trackers | £50 to £200 per device | High: Often weatherproof and rugged | Unlimited (via satellite/cellular) | 6 months to 7 years (or continuous if hardwired) |
| RFID Tags | £0.10 to £10 per tag | Medium to high: Some rugged options | Up to 100 metres (active RFID), few cm (passive) | Passive: none required; Active: 6 months to 2 years |
| Barcodes | £0.01 to £0.10 per label | Low: Susceptible to wear and damage | Line-of-sight only, typically <1 metre | No battery required |