Deploying Utilities Asset Management to Maximising Equipment & Infrastructure Performance
Identify a utilities asset management solution that best matches your asset and infrastructure management needs
What Type of Assets Do You Want To Manage?
By providing key services such as water, gas, and electricity, companies within the utility sector keep the population of households and businesses running smoothly.
So much so, that in 2018 alone the power and energy industry created £86.6bn in economic activity. As well as supporting 620,000 jobs across the UK.
But, the utility sector continues to face multiple challenges that can derail its smooth operations.
One major challenge is the lack of effective asset management when it comes to maintaining mission-critical equipment and ageing infrastructure.
Operational Challenges In the Utilities Industry
In a world of on-demand services and instant access, the ability to obtain utilities is no exception. Households up-and-down the UK expect their access to water, gas, and electricity to be instantaneous and without fault. And, as long as utility processes are running smoothly, there is no need for concern.
But, when issues do occur and disrupt output, it has a major impact. Not only does disruption affect the use of services for paying customers, but, through payouts and maintenance to infrastructure, it also takes a toll on a company’s bottom line.
For instance, from 2014-2018, gas and electricity utility providers paid out a huge £29 million for failing to meet guaranteed service standards.
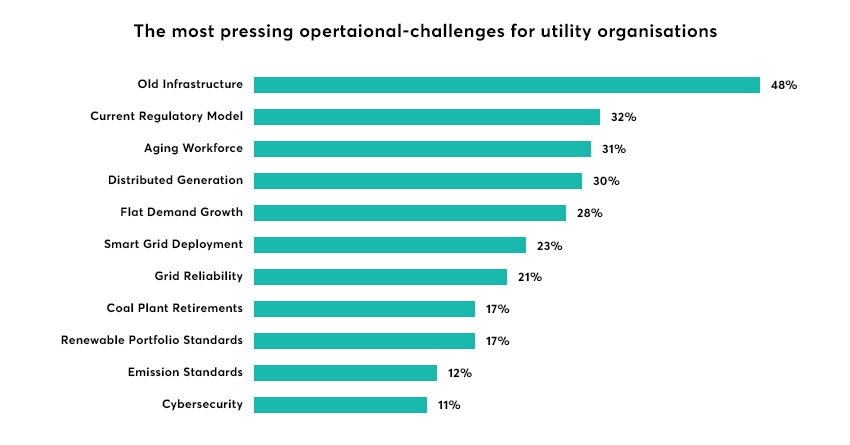
There are a variety of challenges that can affect the production of utilities, including:
- Adhering to constantly-changing government law and regulations
- Switching to clean and renewable energy sources
- Upgrading ageing infrastructure
- Operating with an ageing workforce
- Integrating IoT and AI within existing processes
- Support for the electrification of transport
Although all of these challenges are harmful to the production of utility services, the management and maintenance of assets is one issue that should not be overlooked.
Assets are essential to the power and utilities sector; gas pipelines, substations, storage wells, electrical grids, dams, distribution, and transmission lines – the list goes on. That’s not to mention the data, facilities, buildings, and fleets, either.
If a production-critical asset fails then so does the production of services, which subsequently affects overall profits.
Resolving Challenges With Asset Management
When implemented into industries and organisations that rely heavily on the usage of their assets, an asset management tool can help to better manage and maintain mission-critical equipment across entire operations.
Among various features and tools, an AMS will provide organisations with many benefits, including:
- Tracking asset performance data in real-time based on different KPIs
- Building proactive and preventative maintenance programs
- Tracking asset life cycles from procurement to disposal
- Gaining an accurate ROI for each asset
- Accurately managing inventory control
- Managing and tracking field workers
- Prioritising and scheduling work orders
Improve the Management of Your Utility Assets & Infrastructure
What Type of Assets Are You Looking to Manage?
Giving Power to Your Field Workers
One major benefit of deploying asset management tools into utility operations is being able to collect and store real-time data in one centralised system. Having this data available to workers, managers, and technicians not only speeds up the workflow process but also produces a holistic overview of all valuable assets. Making it particularly useful for field-based workers.
The real-time performance data an asset management tool collects can be achieved with the use of IoT (Internet of Things) devices and includes:
- Asset condition
- Usage history (hours, days, or weeks)
- Work order history
- Latest compliance and licence information
- Maintenance and repair history
Field workers are responsible for call-outs to a business’s most critical assets in the field, such as transmission lines and towers. They’re the technicians that are suitably qualified to maintain and repair ageing infrastructure, effectively minimising the chance of failures and outages. But, without the right data, field staff can only be reactive in their response. This reactive approach can cause high costs in repairs, interrupted service delivery and delays to operations.
By having access to real-time performance data, however, a reactive response quickly transitions into a more proactive one. Not only does access to asset data provide more visibility, but it also connects field workers with employees back at the office. And, similar to field service management, the system containing the performance data can be accessed via a mobile device.
As well as improved time management, access to real-time performance data will drive down the operating costs of each asset. For instance, a company can schedule proactive maintenance work to be carried out during the working week instead of reacting to a failure outside of work hours. This means costly out-call expenses are reduced and reliability is increased.
The collection of real-time data is beneficial in other forms, too:
To Calculate an Asset’s ROI
By tracking assets from procurement to disposal, users can get an idea of their worth to a business’s operations. By knowing each asset’s ROI, and considering operating and maintenance costs, decision-makers can understand if, at the end of an asset’s life cycle, it’s worth replacing or disposing of.
To Analyse the Latest Trends
By collecting large amounts of useful data, businesses can analyse trends that are going to affect their overall output. One example of this is the demand for utilities during different months and seasons throughout the year. Utility companies may notice that gas and electricity is demanded more in the winter period, allowing them to prepare for ramping up production and asset usage. This also allows them to plan for maintenance and repairs during off-peak times, meaning delivery of services isn’t compromised when needed the most.
Leveraging IoT In Your Utilities Operations
Collecting accurate asset performance data is achievable with the use of IoT-enabled devices. These devices, in the form of smart sensors and trackers, talk to each other and relay information back to an asset management system where data is collected and stored.
Before organisations introduced IoT technology into their operations, the process of collecting data was based upon observed judgement and intuition. But, thanks to innovations, data is more accurate and instantly available. This type of digital transformation to help modernize and build smarter infrastructure is expected to cost the utilities sector $14 billion per year throughout 2023.
Introducing IoT alongside asset management solutions can have many benefits for the production of utilities, including:
- Proactively approaching maintenance
- Reducing downtime of essential assets and infrastructure
- Decreasing environmental impacts
- Minimising risks and safety concerns of assets
- Helping to grow the use of renewables such as wind turbines and solar panels
- Providing a more holistic customer-centric approach
Using low-cost sensors in your energy production can also benefit workers in the field. The ability to instantly access real-time data from a mobile device can have both financial and time-management benefits. By installing IoT devices on essential equipment and infrastructure, field workers can gain a real-time view that helps them to determine a proactive approach to repairs and maintenance.
This approach is achievable with data such as an asset’s condition, age, and location. All of which is stored in a centralized asset management database, with the aim to offer a more realistic view of each asset’s health and determine the impact it has on safety, reliability, and risk to a company’s bottom line. IoT technology is also essential for companies who are reliant on the efficiency of their assets and who are looking to reduce their skyrocketing expenses.
Can Smart Meters Help the Utility Companies Deliver Smarter Grids?
Like other IoT devices used in the quest for better asset management and maintenance, smart metres were introduced to drive smarter electrical grids. As well as having a long term target of providing greener energy and improving customer relations.
By providing smart metres to households and businesses, power and utility companies are able to gain a better insight into how public utilities are exploited. The use of gas, water, and electricity by consumers is sent back to the service provider enabling them to build a database to improve future operations. This data then allows them to build a more efficient and reliable production of utilities, among other factors such as:
- Gaining direct consumer feedback
- Being able to offer flexible energy tariffs
- Providing more intelligent energy distribution
As the demand for energy increases year-on-year, such as the electrification of transport and increasing mobile connectivity speeds, collecting accurate data is essential for all utility service providers.